- 使用TensorFlow识别数字验证码的要求
- 一、安装Python和TensorFlow
- 二、复制Mnist(手写数字识别)代码
- 三、运行Mnist程序,完成测试,包括系统自带的测试数据和自己手写数字的数据
使用TensorFlow识别数字验证码的要求
- 安装Python和TensorFlow
- 复制Mnist(手写数字识别)代码
- 运行Mnist程序,完成测试,包括系统自带的测试数据和自己手写数字的数据
- 提交程序和实现报告,报告用pdf格式。
一、安装Python和TensorFlow
1.1. 安装Python
1.1.1 下载Python
从Python官方网站下载与电脑操作系统对应的最新版本的Python。
我下载的是Windows对应的exe文件,运行exe文件安装,安装路径为C:\tool\python3.7.3。
1.1.2 为Python设置环境变量
将C:\tool\python3.7.3和C:\tool\python3.7.3\Scripts添加进系统环境变量。
1.1.3 验证是否安装成功
命令行输入python -V,如果安装成功会提示安装的python的版本,如:
Python 3.7.3
1.2. 安装TensorFlow
1.2.1 安装TensorFlow
使用pip安装,命令行输入pip install tensorflow。
1.2.2 验证是否安装成功
命令行输入pip show tensorflow,安装成功会提示TensorFlow的信息,如:
Name: tensorflow
Version: 2.0.0
Summary: TensorFlow is an open source machine learning framework for everyone.
Home-page: https://www.tensorflow.org/
Author: Google Inc.
Author-email: packages@tensorflow.org
License: Apache 2.0
Location: c:\tool\python3.7.3\lib\site-packages
Requires: grpcio, wheel, tensorflow-estimator, keras-preprocessing, opt-einsum, absl-py, wrapt, numpy, protobuf, astor, termcolor, six, tensorboard, google-pasta, keras-applications, gast
Required-by:
1.3. 安装其他库
在最后的实际编码阶段,发现程序依赖其他的库,如imageio和IPython,因此也需要安装。
1.3.1 安装imageio和IPython
使用pip安装,命令行输入pip install imageio和pip install ipython
1.3.2 验证是否安装成功
命令行输入pip show imageio和pip show ipython,提示对应信息即表示安装成功。
二、复制Mnist(手写数字识别)代码
从初学者的 TensorFlow 2.0 教程,复制并整理手写数字识别的代码,代码如下:
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import tensorflow as tf
# 载入并准备好 MNIST 数据集。将样本从整数转换为浮点数:
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
# 将模型的各层堆叠起来,以搭建 tf.keras.Sequential 模型。为训练选择优化器和损失函数:
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
# 训练并验证模型:
model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5)
model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=2)
# 模型保存
model.save('myminst.model')
三、运行Mnist程序,完成测试,包括系统自带的测试数据和自己手写数字的数据
3.1. 训练模型
运行上述运行代码,执行结果为:
Train on 60000 samples
Epoch 1/5
60000/60000 [==============================] - 6s 104us/sample - loss: 0.2971 - accuracy: 0.9142
Epoch 2/5
60000/60000 [==============================] - 6s 96us/sample - loss: 0.1440 - accuracy: 0.9570
Epoch 3/5
60000/60000 [==============================] - 6s 102us/sample - loss: 0.1073 - accuracy: 0.9671
Epoch 4/5
60000/60000 [==============================] - 6s 99us/sample - loss: 0.0887 - accuracy: 0.9727
Epoch 5/5
60000/60000 [==============================] - 8s 138us/sample - loss: 0.0739 - accuracy: 0.9772
10000/1 - 1s - loss: 0.0389 - accuracy: 0.9771
现在,这个照片分类器的准确度已经达到98%,并且模型已经保存为myminst.model。
3.2. 准备手写数字图片
3.2.1 Mnist中的图片
Mnist中的图片,准备了3张如下:
 、
、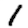 、
、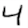
3.2.2 Python模拟生成手写数字图片
使用Python模拟生成手写数字,代码如下:
import random
import os
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
random.seed(3)
path_img = "data_pngs/"
# 生成单张扭曲的数字图像
def generate_single():
# 先绘制一个50*50的空图像
im_50_blank = Image.new('RGB', (50, 50), (255, 255, 255))
# 创建画笔
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(im_50_blank)
# 生成随机数1-9
num = str(random.randint(1, 9))
# 设置字体,这里选取字体大小25
font = ImageFont.truetype('simsun.ttc', 20)
# xy是左上角开始的位置坐标
draw.text(xy=(18, 11), font=font, text=num, fill=(0, 0, 0))
# 随机旋转-10-10角度
random_angle = random.randint(-10, 10)
im_50_rotated = im_50_blank.rotate(random_angle)
# 图形扭曲参数
params = [1 - float(random.randint(1, 2)) / 100,
0,
0,
0,
1 - float(random.randint(1, 10)) / 100,
float(random.randint(1, 2)) / 500,
0.001,
float(random.randint(1, 2)) / 500]
# 创建扭曲
im_50_transformed = im_50_rotated.transform(
(50, 50), Image.PERSPECTIVE, params)
# 生成新的30*30空白图像
im_30 = im_50_transformed.crop([10, 10, 40, 40])
return im_30, num
# 生成手写体数字1-9存入指定文件夹1-9
def generate_1to9(n):
# 用cnt_num[1]-cnt_num[9]来计数数字1-9生成的个数,方便之后进行命名
cnt_num = []
for i in range(10):
cnt_num.append(0)
for m in range(1, n + 1):
# 调用生成图像文件函数
im, generate_num = generate_single()
# 取灰度
im_gray = im.convert('1')
# 计数生成的数字1-9的个数,用来命名图像文件
for j in range(1, 10):
if generate_num == str(j):
cnt_num[j] = cnt_num[j] + 1
# 输出显示路径
print("Generate:", path_img + "/" +
str(j) + "_" + str(cnt_num[j]) + ".png")
# 将图像保存在指定文件夹中
im_gray.save(path_img + "/" + str(j) +
"_" + str(cnt_num[j]) + ".png")
print("\n")
# 输出显示1-9的分布
print("生成的1-9的分布:")
for k in range(9):
print("Num", k + 1, ":", cnt_num[k + 1], "in all")
# generate n times
generate_1to9(1000)
使用这个脚本生成1000张图片,图片分布如下:
生成的1-9的分布:
Num 1 : 99 in all
Num 2 : 113 in all
Num 3 : 118 in all
Num 4 : 113 in all
Num 5 : 115 in all
Num 6 : 111 in all
Num 7 : 117 in all
Num 8 : 93 in all
Num 9 : 121 in all
最后使用这个脚本生成了1000张图片,部分图片如下:
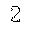 、
、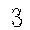 、
、 、
、
3.3. 验证手写数字
验证手写数字的Python代码如下:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
from PIL import Image
# 测试保存的模型,返回预测的结果
def predict(image_path):
# 加载保存的模型
new_model = tf.keras.models.load_model('myminst.model')
img = Image.open(image_path).convert('L').resize((28, 28))
flatten_img = np.array(img) / 255
flatten_img = flatten_img.reshape(28, 28)
x = np.array([1 - flatten_img])
y = new_model.predict(x)
return np.argmax(y[0])
# print('image: {}, predict digit: {}'.format(image_path, np.argmax(y[0])))
def main():
file_dir = 'C:\\tool\\python_tutorial\\tensorflow_tutorial\\images\\' # Mnist数字图片存放路径
# file_dir = 'C:\\tool\\python_tutorial\\tensorflow_tutorial\\data_pngs\\' # Python生成手写数字图片存放路径
list = os.listdir(file_dir)
total = len(list) # 图片总数
error = 0 # 错误总数
error_list = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] # 错误图片是几?
# 遍历图片存放目录下的图片进行预测
for i in range(0, total):
actual_value = int(list[i].split('_')[0])
image_path = file_dir + list[i]
predict_value = int(predict(image_path))
print('actual value: {}, predict value: {}'.format(
actual_value, predict_value))
if actual_value != predict_value:
error_list[actual_value - 1] = error_list[actual_value - 1] + 1
error = error + 1
print('error, error image is ', list[i])
else:
print("total count is:{},error count is:{}".format(total, error))
print("error_list: ", error_list)
print("error rate is: ", error/total)
main()
3.3.1 验证Mnist中的图片
样本共3个,预测结果如下:
actual value: 0, predict value: 0
actual value: 1, predict value: 1
actual value: 4, predict value: 4
total count is:3,error count is:0
error_list: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
error rate is: 0.0
结论:成功识别3张图片里的数字,predict digit分别为0、1、4。
3.3.2 验证Python模拟生成手写数字图片
样本共1000个,预测结果如下:
actual value: 3, predict value: 3
actual value: 4, predict value: 1
error, error image is 4_1.png
actual value: 4, predict value: 1
error, error image is 4_10.png
actual value: 4, predict value: 4
actual value: 4, predict value: 3
...
actual value: 9, predict value: 4
error, error image is 9_97.png
actual value: 9, predict value: 7
error, error image is 9_98.png
actual value: 9, predict value: 3
error, error image is 9_99.png
total count is:1000,error count is:424
error_list: [20, 18, 44, 60, 26, 83, 41, 39, 93]
error rate is: 0.424
结论:总数1000张图片,有424张识别错误,错误率高达42.4%。(我执行了3次,结果都一样)。其中9、6、4等数字识别的错误比较多。但是目前我还不知道问题出在哪里,不知道是模型的问题,还是图片和模型训练使用的图片不符合。
附:
程序目录如下图
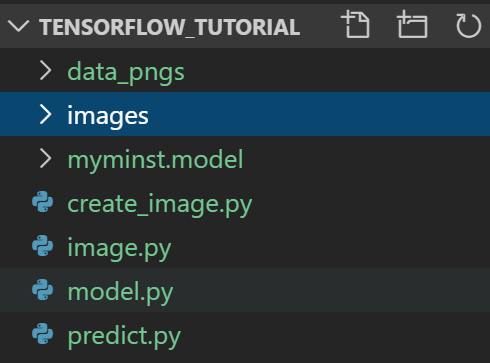
- data_pngs和images分别是存放Python模拟生成的手写数字和Minst中的手写数字的文件夹
- myminst.model是保存的训练过的模型。
- create_image.py是Python模拟生成的手写数字的脚本,代码如下:
import random
import os
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
random.seed(3)
path_img = "data_pngs/"
# 生成单张扭曲的数字图像
def generate_single():
# 先绘制一个50*50的空图像
im_50_blank = Image.new('RGB', (50, 50), (255, 255, 255))
# 创建画笔
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(im_50_blank)
# 生成随机数1-9
num = str(random.randint(1, 9))
# 设置字体,这里选取字体大小25
font = ImageFont.truetype('simsun.ttc', 20)
# xy是左上角开始的位置坐标
draw.text(xy=(18, 11), font=font, text=num, fill=(0, 0, 0))
# 随机旋转-10-10角度
random_angle = random.randint(-10, 10)
im_50_rotated = im_50_blank.rotate(random_angle)
# 图形扭曲参数
params = [1 - float(random.randint(1, 2)) / 100,
0,
0,
0,
1 - float(random.randint(1, 10)) / 100,
float(random.randint(1, 2)) / 500,
0.001,
float(random.randint(1, 2)) / 500]
# 创建扭曲
im_50_transformed = im_50_rotated.transform(
(50, 50), Image.PERSPECTIVE, params)
# 生成新的30*30空白图像
im_30 = im_50_transformed.crop([10, 10, 40, 40])
return im_30, num
# 生成手写体数字1-9存入指定文件夹1-9
def generate_1to9(n):
# 用cnt_num[1]-cnt_num[9]来计数数字1-9生成的个数,方便之后进行命名
cnt_num = []
for i in range(10):
cnt_num.append(0)
for m in range(1, n + 1):
# 调用生成图像文件函数
im, generate_num = generate_single()
# 取灰度
im_gray = im.convert('1')
# 计数生成的数字1-9的个数,用来命名图像文件
for j in range(1, 10):
if generate_num == str(j):
cnt_num[j] = cnt_num[j] + 1
# 路径如 "F:/code/***/P_generate_handwritten_number/data_pngs/1/1_231.png"
# 输出显示路径
print("Generate:", path_img + "/" +
str(j) + "_" + str(cnt_num[j]) + ".png")
# 将图像保存在指定文件夹中
# im_gray.save(path_img + "Num_" + str(j) + "/" + str(j) + "_" + str(cnt_num[j]) + ".png")
im_gray.save(path_img + "/" + str(j) +
"_" + str(cnt_num[j]) + ".png")
print("\n")
# 输出显示1-9的分布
print("生成的1-9的分布:")
for k in range(9):
print("Num", k + 1, ":", cnt_num[k + 1], "in all")
# generate n times
generate_1to9(1000)
- model.py是识别手写数字图片的脚本,代码如下:
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import tensorflow as tf
# 载入并准备好 MNIST 数据集。将样本从整数转换为浮点数:
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
# 将模型的各层堆叠起来,以搭建 tf.keras.Sequential 模型。为训练选择优化器和损失函数:
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
# 训练并验证模型:
model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=20)
model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=2)
# 模型保存
model.save('myminst.model')
- predict.py是使用模型预测识别手写数字图片的脚本,代码如下:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
from PIL import Image
# 测试保存的模型,返回预测的结果
def predict(image_path):
# 加载保存的模型
new_model = tf.keras.models.load_model('myminst.model')
img = Image.open(image_path).convert('L').resize((28, 28))
flatten_img = np.array(img) / 255
flatten_img = flatten_img.reshape(28, 28)
x = np.array([1 - flatten_img])
y = new_model.predict(x)
return np.argmax(y[0])
# print('image: {}, predict digit: {}'.format(image_path, np.argmax(y[0])))
def main():
# file_dir = 'C:\\tool\\python_tutorial\\tensorflow_tutorial\\images\\' # Mnist数字图片存放路径
file_dir = 'C:\\tool\\python_tutorial\\tensorflow_tutorial\\data_pngs\\' # Python生成手写数字图片存放路径
list = os.listdir(file_dir)
total = len(list) # 图片总数
error = 0 # 错误总数
error_list = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] # 错误图片是几?
# 遍历图片存放目录下的图片进行预测
for i in range(0, total):
actual_value = int(list[i].split('_')[0])
image_path = file_dir + list[i]
predict_value = int(predict(image_path))
print('actual value: {}, predict value: {}'.format(
actual_value, predict_value))
if actual_value != predict_value:
error_list[actual_value - 1] = error_list[actual_value - 1] + 1
error = error + 1
print('error, error image is ', list[i])
else:
print("total count is:{},error count is:{}".format(total, error))
print("error_list: ", error_list)
print("error rate is: ", error/total)
main()
本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。